Types of clinical trials
- Pilot studies and feasibility studies.
- Prevention trials.
- Screening trials.
- Treatment trials.
- Multi-arm multi-stage (MAMS) trials.
- Cohort studies.
- Case control studies.
- Cross sectional studies.
Keeping this in consideration, How do you report clinical trials?
How to Report Clinical Trial Results
- Step 1: Review the Requirements for Reporting Results. Review the Results Data Elements Definitions to understand what information is required. …
- Step 2: Complete the Results Modules. …
- Step 3: Upload Supplemental Documentation. …
- Step 4: Release the Record. …
- Step 5: Address PRS Review Comments.
Secondly What are the 5 different types of clinical trials? Types of Clinical Trials. There are several types of cancer clinical trials, including treatment trials, prevention trials, screening trials, supportive and palliative care trials, and natural history studies.
What is an example of a clinical trial?
For example, a clinical trial could involve new drugs, medical devices, biologicals, vaccines, surgical and other medical treatments and procedures. Psycho-therapeutic and behavioural therapies help service changes, preventative care strategies and educational interventions are also examples of clinical trials.
Table of Contents
What needs to be registered on ClinicalTrials?
Which Trials Must Be Registered on ClinicalTrials.gov?
- The trial has one or more sites in the United States.
- The trial is conducted under an FDA investigational new drug application or investigational device exemption.
What is primary completion date in clinical trials?
Primary completion date. The date on which the last participant in a clinical study was examined or received an intervention to collect final data for the primary outcome measure. Whether the clinical study ended according to the protocol or was terminated does not affect this date.
Is a clinical trial a cohort study?
Cohort studies differ from clinical trials in that no intervention, treatment, or exposure is administered to participants in a cohort design; and no control group is defined. Rather, cohort studies are largely about the life histories of segments of populations, and the individual people who constitute these segments.
What is not a clinical trial?
Studies intended solely to refine measures are not considered clinical trials. Studies that involve secondary research with biological specimens or health information are not clinical trials.
What is the difference between a clinical trial and a clinical study?
A clinical trial is one of two main types of clinical studies. A clinical trial tests (or tries out) an intervention — a potential drug, medical device, activity, or procedure — in people. It also is referred to as an interventional clinical study.
Why clinical trials take so long?
The clinical trial process is long – and it’s set up that way so that by the time drugs reach the public, they have been thoroughly evaluated. But the length of the process is one reason why it’s so important for volunteers to take part. Without enough volunteers, up to 80% of clinical trials are delayed.
What defines a clinical trial?
Clinical trials are research studies performed in people that are aimed at evaluating a medical, surgical, or behavioral intervention. They are the primary way that researchers find out if a new treatment, like a new drug or diet or medical device (for example, a pacemaker) is safe and effective in people.
When do you have to register a clinical trial?
Yes, you can register a study on ClinicalTrials.gov at any time. Please note that, in general, Section 801 of the Food and Drug Administration Amendments Act (FDAAA 801) requires Applicable Clinical Trials to be registered within 21 days of enrollment of the first participant.
How do I register for a clinical trial?
How to Register?
- One should first login to CTRI website: www.ctri.nic.in[2]
- Following which, he/she should register himself in CTRI using “Username” and “Password” and create his/her profile. …
- New trial is then added using the CTRI registration data set as detailed in Box no. …
- The above dataset is submitted to CTRI.[2]
Do clinical trials have to be registered?
The International committee of medical journal editors requires registration of trial methodology, but does not require registration of trial results; however, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration Amendments does require researchers to register results.
What is the difference between primary completion date and study completion date?
The Primary and Study Completion Dates may be the same date, but they have different definitions. The Primary Completion Date is based on the data collection for the Primary Outcome Measure. The Study Completion Date is based on the last data collection point for the last patient.
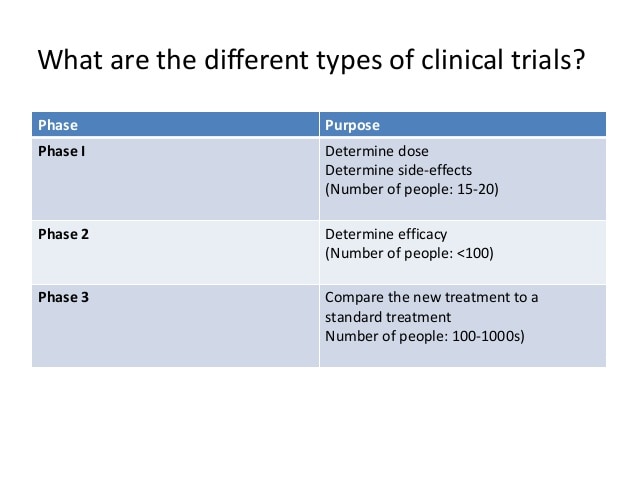
How many phases of clinical trials are there?
Clinical trials have many different phases
There are three phases to each clinical trial before it gets Food Drug Administration (FDA) approval.
What is an example of a cohort?
The term “cohort” refers to a group of people who have been included in a study by an event that is based on the definition decided by the researcher. For example, a cohort of people born in Mumbai in the year 1980. This will be called a “birth cohort.” Another example of the cohort will be people who smoke.
What qualifies as clinical research?
Clinical research is the study of health and illness in people. It is the way we learn how to prevent, diagnose and treat illness.
How do you identify a cohort study?
A well-designed cohort study can provide powerful results. In a cohort study, an outcome or disease-free study population is first identified by the exposure or event of interest and followed in time until the disease or outcome of interest occurs (Figure 3A).
How do you start a clinical trial?
How to Start a Clinical Research Study
- Confirm that a CDA Is In Place (If Appropriate) …
- Assess Protocol Feasibility. …
- Facilitate Contract Preparation. …
- Facilitate Clinical Research Study Budget Plan. …
- Obtain Scientific Review Committee Approval. …
- Compile IRB Submission. …
- Other CHOP Regulatory and Internal Review Committees.
Is a survey considered a clinical trial?
A total of 66 (54%) of 123 surveys were completed; 32/46 (70%) by physicians, 21/59 (36%) by primary care nurses, and 13/18 (72%) by clinical trial nurses. Without a standardized definition, all studies, 12/12, were considered to be clinical trials by at least 50% of respondents.
Do participants in clinical trials get paid?
The answers is yes, you can get paid for study-related time and travel for participating in most clinical trials. While not all studies pay participants, most studies at Meridian pay from $75 to $4,500. The amount is determined by many factors, including, but not limited to: The number of in-person visits required.
Why clinical trials are important?
Clinical trials are important for discovering new treatments for diseases, as well as new ways to detect, diagnose, and reduce the chance of developing the disease. Clinical trials can show researchers what does and doesn’t work in humans that cannot be learned in the laboratory or in animals.
How long should clinical trials take?
Clinical trials alone take six to seven years on average to complete. Before a potential treatment reaches the clinical trial stage, scientists research ideas in what is called the discovery phase. This step can take from three to six years.
How long does it take for a drug to go through clinical trials?
There is no typical length of time it takes for a drug to be tested and approved. It might take 10 to 15 years or more to complete all 3 phases of clinical trials before the licensing stage.
How much do preclinical trials cost?
The average cost of phase 1, 2, and 3 clinical trials across therapeutic areas is around $4, 13, and 20 million respectively. Pivotal (phase 3) studies for new drugs approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) of the United States cost a median of $41,117 per patient.







Add comment