Symptoms
- Difficulty walking or doing normal daily activities.
- Tripping and falling.
- Weakness in your leg, feet or ankles.
- Hand weakness or clumsiness.
- Slurred speech or trouble swallowing.
- Muscle cramps and twitching in your arms, shoulders and tongue.
- Inappropriate crying, laughing or yawning.
- Cognitive and behavioral changes.
Keeping this in consideration, Is ALS hereditary?
Familial (Genetic) ALS
About 5 to 10 percent of all ALS cases are familial, which means that an individual inherits the disease from a parent. The familial form of ALS usually only requires one parent to carry the disease-causing gene.
Secondly What was your first ALS symptom? Early symptoms vary with each individual, but usually include tripping, dropping things, abnormal fatigue of the arms and/or legs, slurred speech, muscle cramps and twitches and/or uncontrollable periods of laughing or crying.
What are the 3 types of ALS?
Causes and Types of ALS
- Sporadic ALS.
- Familial ALS.
- Guamanian ALS.
Table of Contents
What are 3 types of ALS?
Causes and Types of ALS
- Sporadic ALS.
- Familial ALS.
- Guamanian ALS.
What does ALS feel like in the legs?
The first sign of ALS is often weakness in one leg, one hand, the face, or the tongue. The weakness slowly spreads to both arms and both legs. This happens because as the motor neurons slowly die, they stop sending signals to the muscles. So the muscles don’t have anything telling them to move.
What race gets ALS the most?
Less is known about how ALS affects people of different racial and ethnic backgrounds. Some studies suggest that ALS rates are higher among non-Hispanic Caucasians (whites) in Western countries compared with those of African, Asian, and Hispanic descent (minorities) (9–13).
When should you suspect ALS?
Muscle cramps, especially in the hands and feet. Slow or slurred speech, known as bulbar-onset ALS. Trouble chewing, swallowing and/or breathing, Muscle weakness in an arm, a leg, neck or diaphragm.
What can be mistaken for ALS?
A number of disorders may mimic ALS; examples include:
- Myasthenia gravis.
- Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome.
- Lyme disease.
- Poliomyelitis and post-poliomyelitis.
- Heavy metal intoxication.
- Kennedy syndrome.
- Adult-onset Tay-Sachs disease.
- Hereditary spastic paraplegia.
What disease is similar to ALS?
This group includes diseases such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, progressive bulbar palsy, primary lateral sclerosis, progressive muscular atrophy, spinal muscular atrophy, Kennedy’s disease, and post-polio syndrome.
What is the most aggressive form of ALS?
Timothy was diagnosed with bulbar onset sporadic ALS, one of its most aggressive forms. In most cases ALS attacks the large muscle groups first, with a slow progression to fine motor skills, until the person becomes paralyzed and can no longer move, speak, swallow or breathe.
Does ALS come on suddenly?
As I have mentioned before, ALS does not start abruptly. Consider Lou Gehrig. At first he never dreamed he had a disease. That’s the same problem all of our patients face.
How do you rule out ALS?
Tests to rule out other conditions might include:
- Electromyogram (EMG). Your doctor inserts a needle electrode through your skin into various muscles. …
- Nerve conduction study. …
- MRI. …
- Blood and urine tests. …
- Spinal tap (lumbar puncture). …
- Muscle biopsy.
How long does the final stage of ALS last?
Patients will be considered to be in the terminal stage of ALS (life expectancy of six months or less) if they meet the following criteria. (Should fulfill 1, 2, or 3). Patient should demonstrate critically impaired breathing capacity.
Is ALS common in black people?
The incidence of ALS is 1.80 per 100,000 person years among Caucasians, 0.80 among African Americans, 0.76 among Asians, and 0.58 among Hispanics.
Does anyone survive ALS?
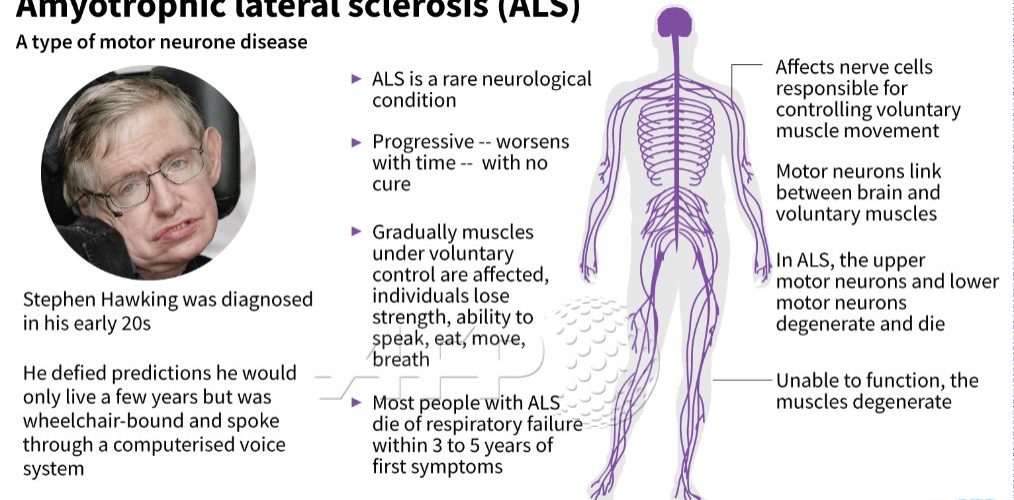
ALS is fatal. The average life expectancy after diagnosis is two to five years, but some patients may live for years or even decades. (The famous physicist Stephen Hawking, for example, lived for more than 50 years after he was diagnosed.) There is no known cure to stop or reverse ALS.
What country has the most cases of ALS?
The prevalence rates of ALS were highest in Uruguay, New Zealand and the United States, and lowest in Serbia, China and Taiwan (Supplementary Tables 1 and 2). The age groups with the highest prevalence rates of ALS were from age 60 to 79.
Is ALS ever misdiagnosed?
Yes, up to 40% of patients are initially told they have another disease, and then it turns out they have ALS. Many conditions can mimic ALS. This type of a diagnostic error is called a false-negative error of diagnosis.
How do doctors rule out ALS?
Abnormalities in muscles seen in an EMG can help doctors diagnose or rule out ALS . An EMG can also help guide your exercise therapy. Nerve conduction study. This study measures your nerves’ ability to send impulses to muscles in different areas of your body.
Does ALS cause pain all over body?
Does ALS cause pain? The answer is yes, although in most cases it does so indirectly. From what we know at this time, the disease process in ALS only affects the nerve cells controlling strength (motor neurons) in the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves.
What vitamins help ALS?
Vitamin B12: Vitamin B12 is essential for the proper development and function of the brain and spinal cord. A Phase 2/3 clinical study (NCT00444613) showed that taking vitamin B12 immediately after symptom onset can slow ALS progression and improve prognosis.
Is MS like ALS?
Multiple sclerosis (MS) and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) are different diseases with some similar features and symptoms. They both: Affect your muscles and your ability to move your body. Attack your brain and spinal cord.
Can ALS be misdiagnosed?
Yes, up to 40% of patients are initially told they have another disease, and then it turns out they have ALS. Many conditions can mimic ALS. This type of a diagnostic error is called a false-negative error of diagnosis.
Has anyone been cured of ALS?
ALS is fatal. The average life expectancy after diagnosis is two to five years, but some patients may live for years or even decades. (The famous physicist Stephen Hawking, for example, lived for more than 50 years after he was diagnosed.) There is no known cure to stop or reverse ALS.
Is there any hope for ALS patients?
About 5,000 people are diagnosed with ALS every year. Most people develop ALS between the ages of 40 and 70, with 55 the average age at diagnosis. There’s no cure.







Add comment